Common Core State Standards may seem complicated if they are new to you; however, these standards have been sensibly designed and organized. Once you understand the logic behind this organization, you’ll be able to navigate the standards with ease. This page explains how to read and understand Common Core State Standards.
An Overview of Standards
There are two classes of Common Core Standards: anchor standards and grade-specific standards. Anchor standards are very broad tasks focused around a general skill. Grade-specific standards are tasks that have been more narrowly defined. Each grade-specific standard is connected to an anchor standard. In this way anchor standards are the backbone of curriculum across all grade levels. Students are expected to demonstrate mastery of each grade-specific standard by the end of the school year. In the next school year, the students will learn from the same anchor standards, but the complexity of the grade-specific standards will have increased.
Grade-Specific Standards
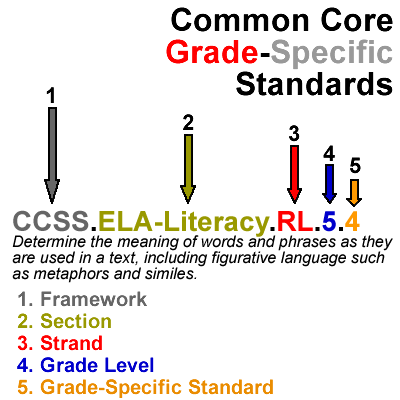
Grade-specific standards are narrowly defined performance tasks that students are expected to complete by the end of the school year. This section explains grade-specific standards. Please refer to the image on the right of this text as I describe the anatomy of a grade-specific Common Core State Standard.
1. Framework
Any time you reference a Common Core State Standard, begin the reference with the following capital letters: CCSS. This initalism stands for Common Core State Standards and it indicates that you are referencing a standard from this framework. Every standard in the Common Core framework begins with these four letters.
2. Section
3. Strand
The ELA-Literacy section is divided into many strands. Each strand has its own set of anchor standards and grade-specific standards. The ELA-Literacy section includes the following strands:
ELA – Literacy Strands
- RL– Reading: Literature
- RI – Reading: Informational Text
- RF – Reading: Foundational Skills
- W – Writing
- SL – Speaking and Listening
- L – Language
- RH – Reading: History / Social Studies
- RST – Reading: Science and Technical Subjects
- WHST – Writing: History, Science, and Technical Subjects
4. Grade Level
This number represents the grade level targeted by the standard. Common Core State Standards are vertically aligned. This means that each grade-specific standard targets roughly the same skill, with varying degrees of rigor, across all grade levels. For example, Reading: Literature standard 3 references characterizations at all grade levels. At the second grade level, students are expected to “describe characters[…] using key details”; while at the eighth grade level, students are expected to “Analyze how particular lines of dialogue or incidents[…] reveal aspects of a character.” Though each tests students’ knowledge of characterizations, the task for eighth grade students is much more rigorous. This demonstrates that grade-specific standards increase in complexity as the grade level increases.
5. Grade-Specific Standard
Grade-specific standards are clearly worded tasks that students should be able to complete by the end of each school year. Each grade-specific standard is aligned to an anchor standard. The last number in a grade-specific standard will match up with the last number in the anchor standard to which it is aligned.
Understanding Anchor Standards
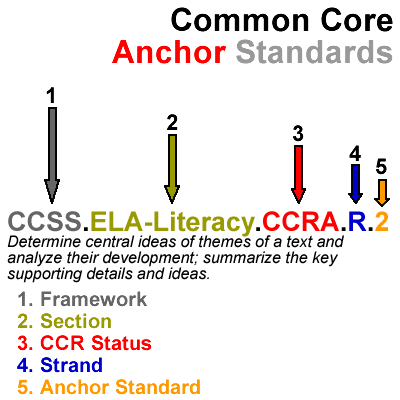
1. Framework
As with the grade-specific standards, under Common Core State Standards the framework is always referenced as CCSS.
2. Section
The section will either be ELA-Literacy or Math, depending on the set of standards that you are using.
3. CCR Status
The CCR status is represented by the initialism CCRA, which stands for College and Career Readiness Anchor. As far as I know, the CCR status is marked as CCRA in every anchor standard. The CCR Status serves little purpose other than to clearly indicate that you are looking at an anchor standard.
4. Strands
The anchor standards have the following strands:
Strands for ELA-Literacy Anchor Standards
- R – Reading
- W – Writing
- SL – Speaking and Listening
- L – Language
5. Anchor Standard
Anchor standards are broadly defined tasks based on a general skill. Each grade-specific task is connected to an anchor standard.
I hope this page has helped you to better understand how Common Core State Standards are structured and organized. If you have any questions or comments, please leave them below.
Looking for Something Else?
Common Core Lesson and Unit Plans
Skill Based Online Reading Tests
All Reading Worksheets

Enas
/ August 26, 2023You’ve literally saved my life. God bless you.
abderrazak nir
/ April 2, 2017thank you so much for these activities . in fact my language level is improving due to reading texts and solving its exercises/thank you again.
Mr. Morton
/ April 6, 2017You are so welcome. Thank you for visiting and taking the time to comment.
looyee
/ April 5, 2014need further info about reading skills